What is CBD?
Products containing CBD have become more accessible for consumers over the last year. CBD has made its way into several products, such as lotions, bath bombs, oils and now—food. Foods and beverages like beer, coffee, cookies, and even dog treats, are being infused with CBD to meet the latest trend.
A quick review of important dates regarding CBD:
- In June of 2018, the FDA approved the first drug to treat epilepsy containing CBD.
- The 2018 Farm Bill passed on Dec. 20, removing industrial hemp as a controlled substance under federal law.
- On May 31, 2019, the FDA held a public hearing to discuss regulations on CBD in food.
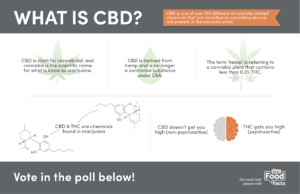
CBD is short for cannabidiol and cannabis is the scientific name for what is commonly known as marijuana. We’ve reached out to expert Dr. Norbert Kaminski, Director for the Institute for Integrative Toxicology and Interim Director for the Center for Research on Ingredient Safety at Michigan State University, to provide insight on this topic.
What is CBD?
Dr. Kaminski: “CBD is one of over 100 different structurally related chemicals that are classified as cannabinoids and are present in the cannabis plant. The different cannabinoids have chemical structures that are similar to one another, and that is how they have been classified.”
How are cannabis, hemp, CBD and THC connected?
Dr. Kaminski: “The term ‘hemp’ is really referring to the cannabis plant that has less than 0.3% THC by dry weight. So, it has been cultivated to have low amounts of THC. Hemp and cannabis can be used interchangeably, but hemp has been bred to have very low amounts of THC. Technically, CBD is extracted from hemp. If CBD is extracted from cannabis that has more THC than that 0.3% of dry weight, then it now becomes a controlled substance as defined by the DEA. As long as CBD is extracted from hemp, then it is not controlled by the DEA and the federal government.”
- Cannabis — Refers to the plant commonly known as marijuana
- Hemp — Refers to the cannabis plant bred to contain less than 0.3% THC
- CBD — Derived from hemp and is no longer a controlled substance under DEA
- THC — The primary psychotropic ingredient present in cannabis
Are there any health concerns that people should keep in mind when choosing to use CBD?
Dr. Kaminski: “Yes, specifically the purity and how have these products been prepared. The quality control for the preparation of these products is a major concern. It seems like these products are popping up on the market almost every day. I think we need more general toxicology evaluations around CBD. Whether it’s safe or not — ultimately it will have to do with the level of exposure.”
Can you get “high” from eating CBD-infused foods?
Dr. Kaminski: “You cannot get ‘high’ from ingesting CBD. The way that individuals get high from cannabis is that the major psychotropic compounds in cannabis, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), bind proteins called receptor (cannabinboid receptors), which are very abundant in the brain. CBD does not bind to these receptors and therefore does not produce a high. Now, if your product was contaminated with THC, you certainly could get high. But, if the product just contains CBD, then no.”
CBD is a naturally occurring, active ingredient found within hemp and contains very little THC. You cannot get “high” from CBD. As the CBD market is expanding, consumers should be aware of the facts regarding this unique ingredient.